
Process improvement is a key area in any industry, whether it is business, law or healthcare. Quality Improvement (QI) is a framework used to improve processes and systems. In healthcare, it translates to a better quality of care, healthier patients and safer medication practices. There are a variety of Quality Improvement tools that can be used to prevent incidents and improve processes to solidify your team’s patient safety efforts. Here we review four popular QI tools and how they can be used to improve safety in your pharmacy.
1. Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis (RCA) is the process of discovering the root causes of problems in order to identify underlying issues and finding proper solutions. It focuses on what happened, why it happened, and how it happened. After finding the root cause, the incidents become preventable.
One of the most popular methods of RCA is the “5-Whys Analysis”. This problem-solving process requires us to look at a problem and ask “why” and “what caused this problem”. The first answer will prompt four additional “why” questions.
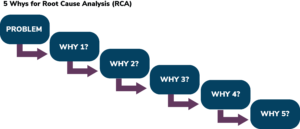
When should I use it? Root cause analysis should be used when you want to identify the root cause of an incident or near-miss. Be careful to answer objectively and not subjectively. Focus on the process and not the people.
2. Fishbone Diagram (or Cause and Effect Diagram)
A cause and effect diagram, also known as an Ishikawa or fishbone diagram is a graphic tool used to explore and visually display the possible causes of a certain effect. It also showcases a variety of factors contributing to the outcome. The diagram allows us to identify areas where improvement is needed. Typically, fishbone diagrams include six major causal factor categories: Man, Material, Method, Measurement, Machine, and Mother Nature.
Each major category then includes any associated events or circumstances where pharmacy staff are involved (e.g. misread prescription), and finally the circumstances relating to the pharmacy itself (e.g.. no training, malfunctioning printer), that can help determine where something went wrong.

When should I use it? Fishbone diagrams are often used in conjunction with the ‘5 Whys’ tool to identify the root cause of an incident or near-miss event.
3. Process Mapping
Process mapping showcases the step-by-step flow of the process, its timing, handoffs, and identifying outputs that can be visualized, measured, and studied. Process maps display the exact steps within any process, as well as individuals who are responsible for each milestone. Visualizing the process step-by-step helps reduce inefficiencies or effort duplication. It is a great team exercise that you can post in a staff room and have multiple people add sticky note comments to for a collaborative and inclusive approach to improvement plans.
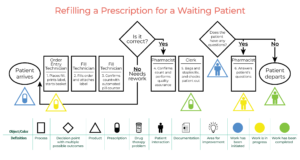
Source: https://wp.media.unc.edu/changemgmt/valuestream/
When should you use it? When a process is breaking down, complicated or unclear, and there is no defined ownership of each step. Start with what is actually happening today, then add change points that would improve it to what it should be.
4. Plan-Do-Study-Act (Pharmapod recommended QI tool)
The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) consists of developing a plan to test the change (Plan), carrying out the test (Do), observing and learning from the consequences (Study), and determining what modifications should be made to the test (Act). PDSA cycles are intended to be quick and easy to measure the impact of the change. To implement PDSA in your pharmacy:
- Set out the objective for the test and your theory of the outcome
- As you begin to execute the plan, document your findings
- Once the plan is executed, analyze the findings and compare the collected data to your initial prediction
- After analyzing the data, develop a plan for a new test with new modifications and repeat starting with Step 1 until a desired outcome is achieved.

When to use Plan-Do-Study-Act? When you are not certain which variable is responsible for the outcome, or you want to test your hypothesis of the process improvement.
Quality improvement is a team effort
Teamwork is critical to success when implementing any quality improvement framework.
Conducted as a team activity, any of the above quality improvement tools can spark discussion about pharmacy processes and ideas on how to improve it. A quality improvement workshop session has to be a curiosity exercise and not a blame game to ensure participation, honesty and engagement among your teammates.
+ + +
Pharmapod’s platform helps your pharmacy team to easily document medication-related events, offering insight into how to improve processes and enhance safety moving forward.
Learn about quality improvement tools and how to simplify incident management reporting in your practice in our on-demand webinar, Mission Impossible: Can Reporting Medication Errors and Learning from Data be Easier?
Pharmapod is a member of the Think Research family of companies.
Share this Article
Recent Articles
Why More Medication Incident Reports Indicates a Safer Pharmacy Environment
It’s a common misconception in pharmacies that having many medication incident reports indicates the pharmacy environment is unsafe. Actually, the opposite is true. The more
On-Demand Webinar: Pharmapod Safety Series – Creating Your Own Safety Net
From drug shortages to high volumes of walk-in traffic, environmental distractions are unavoidable in pharmacies – but they’re also the #1 contributing factor to medication
Think Research’s Pharmapod Adopted in University and Colleges Across Canada to Teach Foundations of Medication Safety
TORONTO, ON – February 27, 2024 – Think Research Corporation (TSXV: THNK) (“TRC” or the “Company“), a company focused on transforming healthcare through digital health



